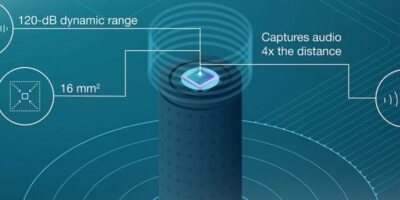
Engineers can now achieve a 120dB dynamic range for clear, high-fidelity audio in smart home applications, says Texas Instruments (TI) as it introduces the TLV320ADC5140audio ADC. It can capture clear audio up to four times farther away than competing devices, claims TI. The TLV320ADC5140 is the industry’s smallest quad-channel audio ADC with this level of performance, says the company. It is part of a family of three TI Burr-Brown audio ADCs that enable low-distortion audio recordings in loud environments and far-field, high-fidelity recordings in any environment.
In smart home systems, a limited number of microphones and restricted signal processing capability make it difficult to capture and understand voice commands in loud environments. To meet this challenge, the TLV320ADC5140 enables engineers to improve audio capture from across rooms and boost recognition of soft-spoken commands in applications such as high-end smart speakers, sound bars, wireless speakers, high definition TVs, IP network cameras, tele-conferencing systems and smart appliances.
The TLV320ADC5140 provides clear audio capture in any environment in beamforming systems, says TI. It has a built-in 120dB dynamic range enhancer (DRE). At a system level, the DRE scheme boosts low-volume audio signals while maintaining low-distortion recordings, even at close proximity to the speaker output. The DRE also improves far-field, high-fidelity recordings in all environments.
The TLV320ADC5140 is believed to be the first ADC that fully supports the latest high signal-to-noise-ratio microphones with greater than 106dB dynamic range.
Up to four analogue or eight digital microphones can be converted and programmable features such as gain and phase calibration can equalise microphone-array mismatches. Other features include a programmable gain amplifier, high-pass filters, channel mixing, and linear phase or ultra-low-latency decimation filters.
The TLV320ADC5140 enables engineers to offload digital signal processing tasks, to shrink the size of designs while maintaining system reliability and minimising power consumption to only 9.5mW per channel at 48kHz.
The TLV320ADC5140 is available in a 4.0 x 4.0mm, 24-pin wafer quad flatpack no-lead (WQFN) packaging. The TLV320ADC5140 quad-channel 768-kHz TI Burr-Brown audio ADC evaluation module, the ADC5140EVM-PDK, is also available.