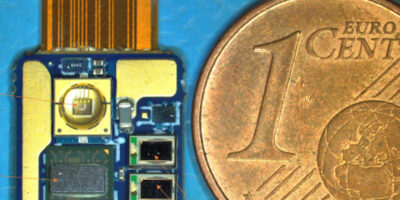
At MWC21, LiFi specialist, Oledcomm, unveiled Gigabit OFE, an ASIC that turns any mobile device into a Li-Fi-powered device, says the company.
Li-Fi (light fidelity) allows devices to be connected to each other using light. Li-Fi transmits data by modulating light signals from a light source, the light signals are received and converted into data using a dongle connected to the device.
The 1.5 x 2.5mm ASIC can be seamlessly integrated into smartphones, laptops and tablets, says the company, eliminating the need for the dongle. It can be coupled with photodiodes and light source like LED or VCSEL to achieve a 1Gbit per second point to point connection at a distance of one to five metres. The OFE can be used with a G.99991 baseband as well as a 802.11 baseband which is already present in most of today’s mobile devices.
Benjamin Azoulay, president of Oledcomm, said the Gigabit OFE will radically change the end user experience. Dongles will no longer be required as the Li-Fi is natively integrated into devices, bringing a “light-based, fast, secure and healthy wireless connectivity anywhere WiFi/4G/5G radio waves are not suitable”.
Oledcomm is based in Paris, France and specialises in data exchange solutions using light (Li-Fi). It designs complete solutions for Li-Fi operation, including microcontrollers (modems), Li-Fi photoreceivers (dongles and bridges) and software platforms (Li-FiCloud and software development kits).
The potential market for Li-Fi is huge, says the company: with 14 billion points of light worldwide which could become a powerful, safe and radio-free communication network.
Oledcomm holds more than 28 patents (supported by France Brevets) and has partnered with Ariane Group, Thales Alenia Space, OneWeb, French space agency CNES and Ford.
In January 2018, Oledcomm launched MyLiFi, the first luminaire accessible to the general public, the following year, it launched the LiFiMAX website, the first internet access point through invisible light.
In October 2019, an Air France A321 plane equipped with Oledcomm Li-Fi modems flew from Paris to Toulouse.
Oledcomm is certified ISO9001 and ISO14001.