USB Type-C is a relatively new, high power USB peripheral standard used in computer and portable electronic devices. The USB Type-C standard has driven changes in the USB power delivery specification, allowing for increased bus voltages (up to 20V) and current delivery capability (up to 5A) from the long-standing 5V USB standard. Connected USB-C devices can recognise each other and negotiate a bus voltage – from the default 5V USB output to several higher preset voltage steps – for faster battery charging and higher power delivery where needed, up to 100W.
The simple, compact buck regulators and linear regulators used in battery chargers that require only USB 5V at 500mA to 2A do not sufficiently cover the full range of Type-C USB power. The increased voltage range, 5V to 20V, of Type-C USB power delivery requires more than just step-down voltage conversion from 9V to 36V (or 60V) automotive batteries, or other charging sources. An adjustable buck-boost converter is needed with the ability to both step-up and step-down the input-to-output voltage.
Additionally, for high power automotive USB chargers, a buck-boost converter should support a 10A or higher peak switch current rating and offer low EMI performance. The ability to set the switching frequency outside the AM radio band and maintain a small solution size are sought-after features. High voltage monolithic converters (with onboard switches) are not capable of sustaining such high peak switch currents without burning up.
The LT8390A is a unique 2MHz, synchronous 4-switch buck-boost controller. At 2MHz switching frequency, it can deliver output voltages between 5V and 15V (up to 45W at 3A) to provide power to a connected USB-C device from a car battery. This high controller switching frequency keeps the solution size small, the bandwidth high, and the EMI outside of the AM radio band. Both spread spectrum frequency modulation and low EMI current-sense architecture help LT8390A applications pass the rigors of the CISPR 25 Class 5 automotive EMI standard.
High Power Density Conversion: Size (and Power), Efficiency, Heat
The design of a voltage regulator system operating in an automotive or portable electronics environment is constrained by the space required for the circuit, as well as the heat it generates during operation. These two factors impose an upper bound of achievable power levels while operating within the given design constraints.
Increasing the switching frequency of a design allows for the use of smaller inductors, which is often the largest footprint component in wide input voltage 4-switch buck-boost voltage regulator designs. The LT8390A’s 2MHz switching frequency capability enables the use of a much smaller inductor size than a 150kHz or 400kHz design. A complete design is shown in Figure 1. Along with a smaller inductor, this solution uses only ceramic output capacitors, eliminating the need for bulky electrolytic capacitors. All the components necessary for this design, including the IC, are contained within a small, 1″ inch square footprint, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Efficient, low EMI USB Type-C power solution that fits in a 1″ square.
Figure 2 shows a 45W LT8390A solution using AEC qualified components. This design experiences a maximum temperature increase of 65°C from the ambient temperature, as shown in Figure 3. Even with the small solution size, the LT8390A system boasts a peak efficiency of 94% while delivering a 45W output, and deviates in efficiency by less than 10% over the input range for each output voltage created, shown in the graphs in Figure 4.
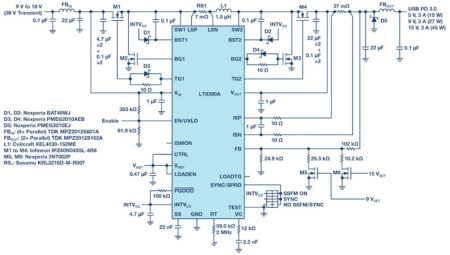
Figure 2. This LT8390A voltage regulator solution provides up to 3A at selectable 5V, 9V, or 15V low EMI outputs using AEC qualified
MOSFETs, magnetics, and capacitors.
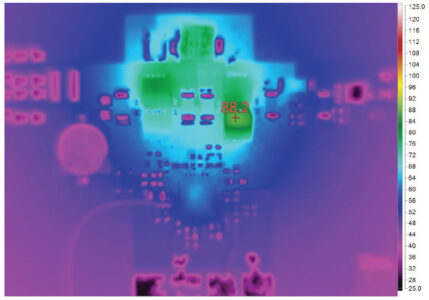
Figure 3. While generating 45W of output power, this small circuit’s greatest temperature rise is only 65°C above ambient temperature.
Low EMI for Automotive Applications
The LT8390A has several unique EMI mitigating features that enable high power conversion with low noise performance, which simplifies its implementation in automotive systems. A notable difference between LT8390A and alternative 4-switch controllers is the placement of the inductor current sensing resistor. Most 4-switch buck-boost controllers tend to use a ground-referred current sensing scheme to obtain switch current information, whereas the LT8390A places its current sense resistor in-line with the inductor. By placing the sensing resistor in-line with the inductor, it is effectively removed from both the buck and boost hot loops, shrinking the loops in size and improving the EMI performance.
Along with the architectural advantage of the inductor sensing resistor placement, the LT8390A has built-in spread spectrum frequency modulation to further reduce EMI generated by the controller. Furthermore, the switching edge rate is controlled on both the buck and boost power switches using only a few discrete components to slow the turn-on of the MOSFETs, ensuring the proper balance of high frequency EMI reduction and temperature rise in the power switches. With these EMI-reducing features, the only filtering needed to meet CISPR 25 compliance is taken care of by small ferrite filters on the input and output rather than large ferrite cases and bulky LC filters. The solution shown in Figure 1 was designed using only AEC-Q100 components.
Seamless Output Voltage Transitions
The LT8390A’s output voltage can be adjusted without shutting down the converter by using logic-level signals to drive MOSFETs that adjust the resistor divider off the output to change the set voltage. A USB PD source controller device with GPIO pins can be used in conjunction with the LT8390A system to facilitate the negotiation process between host and USB-connected device and to set the desired bus voltage.
Figure 5 demonstrates how smoothly the output of the LT8390A system transitions from one output voltage to another. When powered from a 12V input source, each transition to an increased output voltage takes at most 150µs to settle, as measured from the rising edge of the digital control signal. During these changes in the output voltage, the buck-boost controller goes through mode transitions – between buck, boost, and buck-boost operation – depending on the relation of input to output voltages. These mode transitions are performed in a controlled manner, preventing excessive overshoot or sagging of the output voltage.
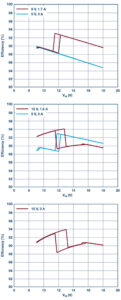
Figure 4. The LT8390A voltage regulator system remains in the 94% to 84% efficiency range across all output voltages generated when powered from an automotive SLA battery.
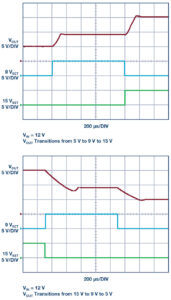
Figure 5. The output of the LT8390A system smoothly transitions between 5V, 9V, and 15V outputs while maintaining continuous power deliver to the output.
Expanding Beyond 45 W
To push the output power level beyond 45W requires operating at a lower switching frequency to reduce switching losses, which might otherwise thermally stress the MOSFETs at this power level. As an alternative to the LT8390A, the LT8390 operates between 150kHz and 600kHz with the same feature set as LT8390A – allowing low EMI, high power buck-boost designs. A 400kHz LT8390 system, utilising a larger inductor and output capacitor, easily achieves 100W of output power from an automotive battery input with acceptable temperature rise. Figure 6 illustrates the power capabilities of the LT8390A and LT8390 product line from various battery-powered inputs.
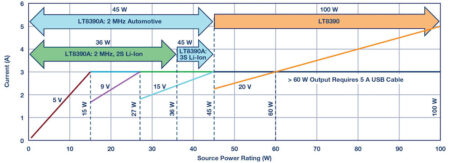
Figure 6. The LT8390A and LT8390 cover a wide range of output power levels for USB power delivery.
Conclusion
The new USB standard for voltage regulators powering connected devices permits higher power transfer by increasing the output voltage range and current delivery that regulators can provide. Portable and automotive battery-powered USB-C charger devices require a wide VIN/VOUT buck-boost regulator to deliver a bus voltage above or below the input voltage. The LT8390A provides up to 45W of output power in a small footprint, made possible by its 2MHz switching frequency. For power levels exceeding 45W, the LT8390 can be used with a slightly larger solution size and lower switching frequency.
By Kyle Lawrence
Kyle Lawrence [kyle.lawrence@analog.com] is an applications engineer at Analog Devices. He is responsible for the design and testing of a variety of dc-to-dc converters, including 4-switch buck-boost voltage regulators and LED drivers targeting low EMI automotive applications. Kyle received his B.S. degree in electrical engineering from the University of California, Santa Cruz in 2014.