Light sensors halve smartphone apertures
Able to reduce LED emitter-to-sensor gap to just 1.0mm, the TMD2620 proximity sensor and TMD2725 ALS modules also eliminate optical crosstalk, says ams.
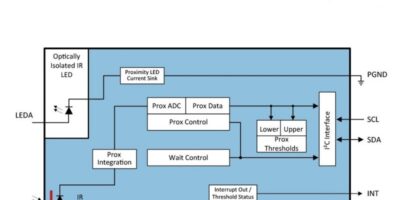
The TMD2620 proximity sensor (pictured) or the TMD2725, which is a combined proximity and ambient light sensor, enables phone manufacturers to reduce the aperture’s size by as much as 50%, says the company to improve aesthetic appeal, especially in devices with a white or light-coloured bezel. The TMD2620 and TMD2725 enable aperture size as small as 1.4 and 2.0mm respectively.
Both have an optical module packaging which allows the emitter, an infra-red LED, and photodiode to be placed 1.0mm apart. Lenses on top of the emitter and sensor and an optical barrier are also claimed to help minimise crosstalk, caused by reflections from the surfaces of the cover glass. Offset adjustment registers eliminate the effect of any residual crosstalk from the module’s proximity calculations. Automatic ambient light subtraction further enhances the accuracy of proximity measurements. The ability to measure up to a range of 100mm is comparable to laser-based solutions, claims the company.